Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.03003
Overview
- A Multi-Object Rectified Attention Network for Scene Text Recognition (MORAN) can read rotated, scaled and stretched characters.
- MORAN = multi-object rectification network (MORN) + attention-based sequence recognition
network (ASRN)
- MORN: works to rectify image. weakly supervise training led by ASRN.
- ASRN: works to read text.
Contributions
- MORAN framework
- The subnetwork MORN which trained in weakly supervised way is flexible cause there is no constraints
- Fractional pickup method: used for training of attention based decoder in ASRN
- Curriculum learning strategy
limitation

- With complicated background, MORAN can mistakenly regards the background as foreground. MORAN can rectify irregular text with small curve angles.
- As MORAN is not designed for vertical text, it focuses more on horizontal irregular text.
- MORAN needs text detector. Without text detector, MORAN is not end-to-end scene text recognition system.
Related Work
Flow of recognition of scene text
- Pattern features extracted by a neural network based on the sliding window method
- Combine of CNN for spatial features of image and RNN for context of features
- RCNN (end-to-end trainable network with both CNNs and RNNs) and CTC loss
- Attention mechanisms
- recursive recurrent network with attention modeling
- two-dimensional attention mechanism
- focusing attention network (FAN) to correct shifts in attentional mechanisms and achieved more accurate position predictions.
Two kind of method for irregular text recognition
- Bottom-up: searches for the position of each character and then connects them.
- two-dimensional attention mechanism for irregular text
- Based on the sliced Wasserstein distance, the attention alignment loss is adopted in the training phase, which enables the attention model to accurately extract the character features while ignoring the redundant background information.
- arbitrary-orientation text recognition network
- uses more direct information of the position to instruct the network to identify characters in special locations.
- two-dimensional attention mechanism for irregular text
- Top-down: matches the shape of the text, attempts to rectify it, and reduces the degree of recognition difficulty.
- STAR-Net
- used an affine transformation network that transforms the rotated and differently scaled text into more regular text.
- ResNet is used to extract features and handle more complex background noise.
- RARE
- regresses the fiducial transformation points on sloped text and even curved text, thereby mapping the corresponding points onto standard positions of the new image.
- Using thin-plate-spline to back propagate the gradients, RARE is end-to-end optimized.
- STAR-Net
MORAN use Top-down approach, fractional pickup training, curriculum learning strategy
Methodology
MORAN is consist of MORN and ASRN. MORAN is trained with curriculum learning strategy.
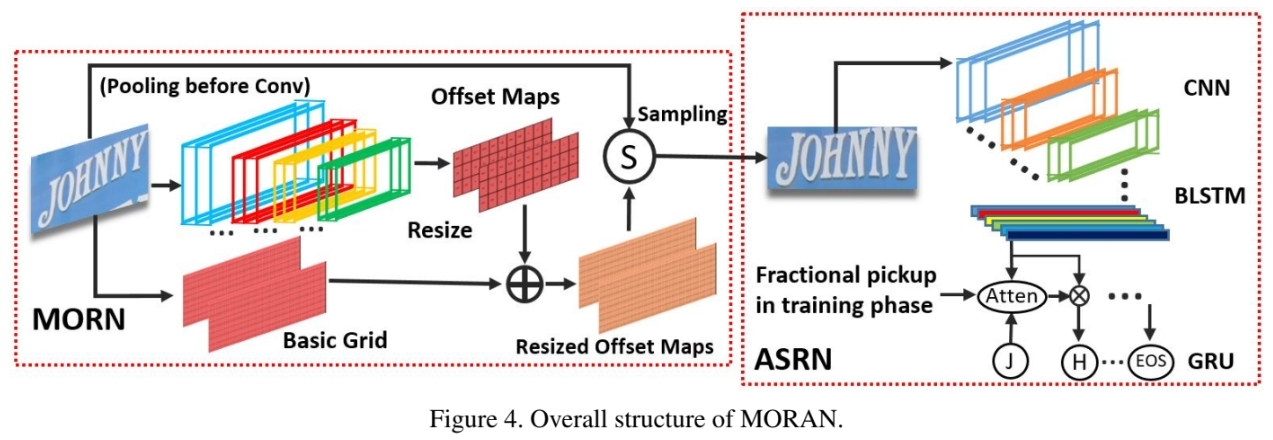
MORN
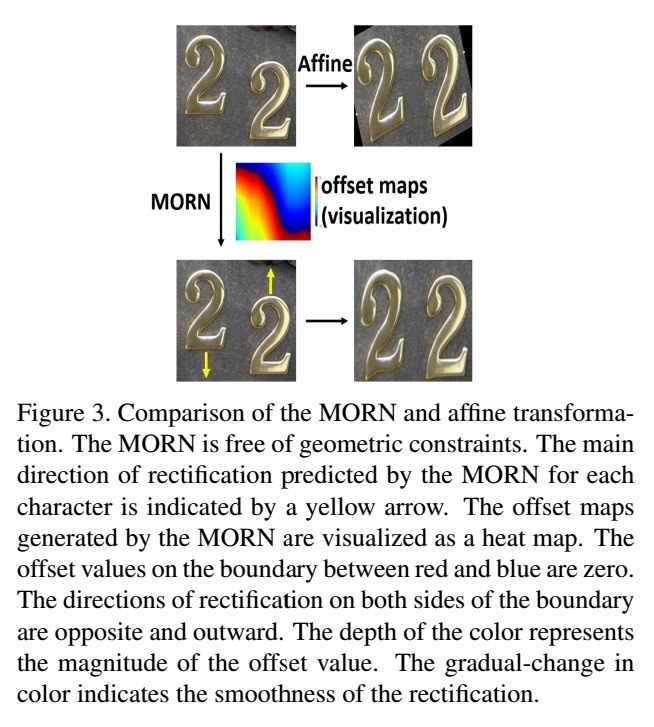
MORAN which is trained in weakly supervised way learn to make offset of image’s each part to rectify text image.
 |
 |
Other methods
- Affine transformation which has geometric constraints can not cover all complicated deformations.
- Deformable has no geometric constraints. Authors attepted to combine recognition network with deform conv, but the network sometimes fail to converge. Best accuracy with deform conv that authors archived is far behind the SOTA result.
→ MORN makes offset to rectify with no geometric constraints.
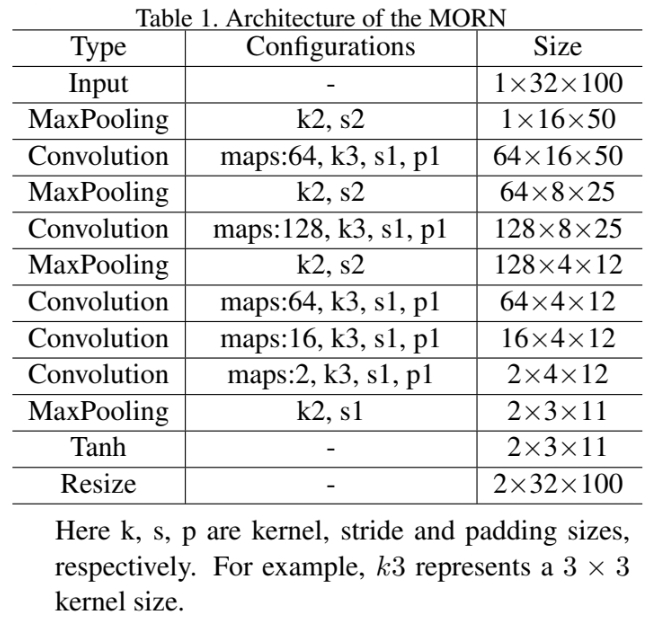
Architecture
- The character details for classification are not necessary. We hence place a pooling layer before the convolutional layer to avoid noise and reduce the amount of calculation.
- The MORN divides the image into several parts and then predicts the offset of eachpart.
- The offset maps contain two channels, which denote the x-coordinate and y-coordinate respectively.
- As blow equation is differentiable, the MORN can back-propagate the gradients. (I, I’ are input image, rectified image and (i,j), (i’,j’) are origin position, position made by MORN)
Advantage
- The rectified images are more readable owing to the regular shape of the text and the reduced noise.
- The MORN is more flexible than the affine transformation.
- The MORN is more flexible than methods using a specific number of regressing points.
- The MORN does not require extra labeling information of character positions.
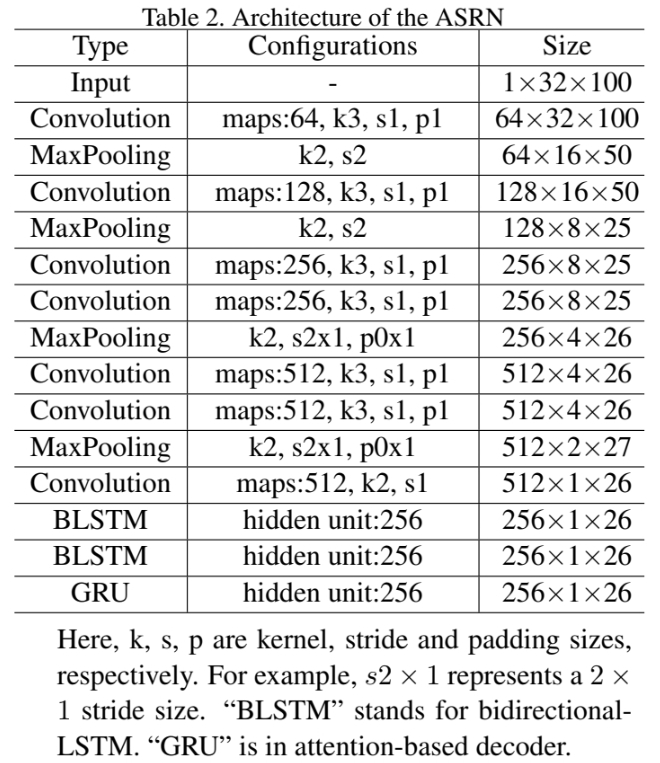
ASRN
ASRN is CNN-LSTM framework followed by one attention decoder with fractional pickup.
The decoder in the ASRN learns the matching relationship between labels and target characters in images. It is a data-driven process.
 |
 |
Fractional Pickup
Often, the decoder is likely to be deceived into focusing on ambiguous background regions inpractical applications.
To solve this, propose a training method called fractional pickup that fractionally picks up the neighboring features in the training phase.
An attention-based decoder trained by fractional pickup method can perceive adjacent characters. The wider field of attention contributes to the robustness of the MORAN.
-
Variation of Distribution
As fractional pickup randomly adds current and past attention weight to make current attention weight for use, even for the same image, the distribution of current attention weight changes every time step in training phase.
This randomness avoids over-fitting and contributes to the robustness of the decoder.
-
Shortcut of Forward Propagation
Fractional pickup provides more information about the previous step and increases the robustness for the bidirectional-LSTM in the ASRN.
-
Broader Visual Field
Owing to the disturbance, back-propagated gradients are able to dynamically optimize the decoder over a broader range of neighboring regions.
It extracts features not only of the target characters, but also of the foreground and background context. As demonstrated in Fig. 6, the expanded visual field enables the MORAN to correctly predict target characters. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to adopt a shortcut in the training of the attention mechanism.
Curriculum learning strategy
End-to-end training consumes considerable time. We found that the MORN and ASRN can hinder each other during training. A MORN cannot be guided to rectify images when the input images have been correctly recognized by the high-performance ASRN and vice versa.
First Stage for ASRN
- We optimize the ASRN by using regular training samples.
- The ASRN is first trained with these regular samples. Then, we simply crop every text using a minimum circumscribed horizontal rectangle to obtain irregular training samples.
Second Stage for MORN
We fix the parameters of ASRN trained as fisrt stage, and stack it after the MORN. If the transformation of the MORN does not reduce the difficulty of recognition, few meaningful gradients will be provided by the ASRN. The optimization of MORN would not progress. Only the correct transformation that decreases difficulty for recognition will give positive feedback to the MORN.
Third Stage for End-to-end Optimization
Authors connect them for joint training in an end-to-end fashion. Joint training enables MORAN to complete end-to-end optimization and outperform state-of-the-art methods.