website: https://interpretablevision.github.io/
Lecture 1 by Bolei Zhou: Exploring and Exploiting Interpretable Semantics in GANs. video, slide, bili
Lecture 2 by Zeynep Akata: Modeling Conceptual Understanding in Image Reference Games video, slide, bili
Lecture 3 by Ruth C. Fong: Understanding Deep Neural Networks video, slide, bili
Lecture 4 by Christopher Olah: Introduction to Circuits in CNNs. video, slide, bili
Lecture 1
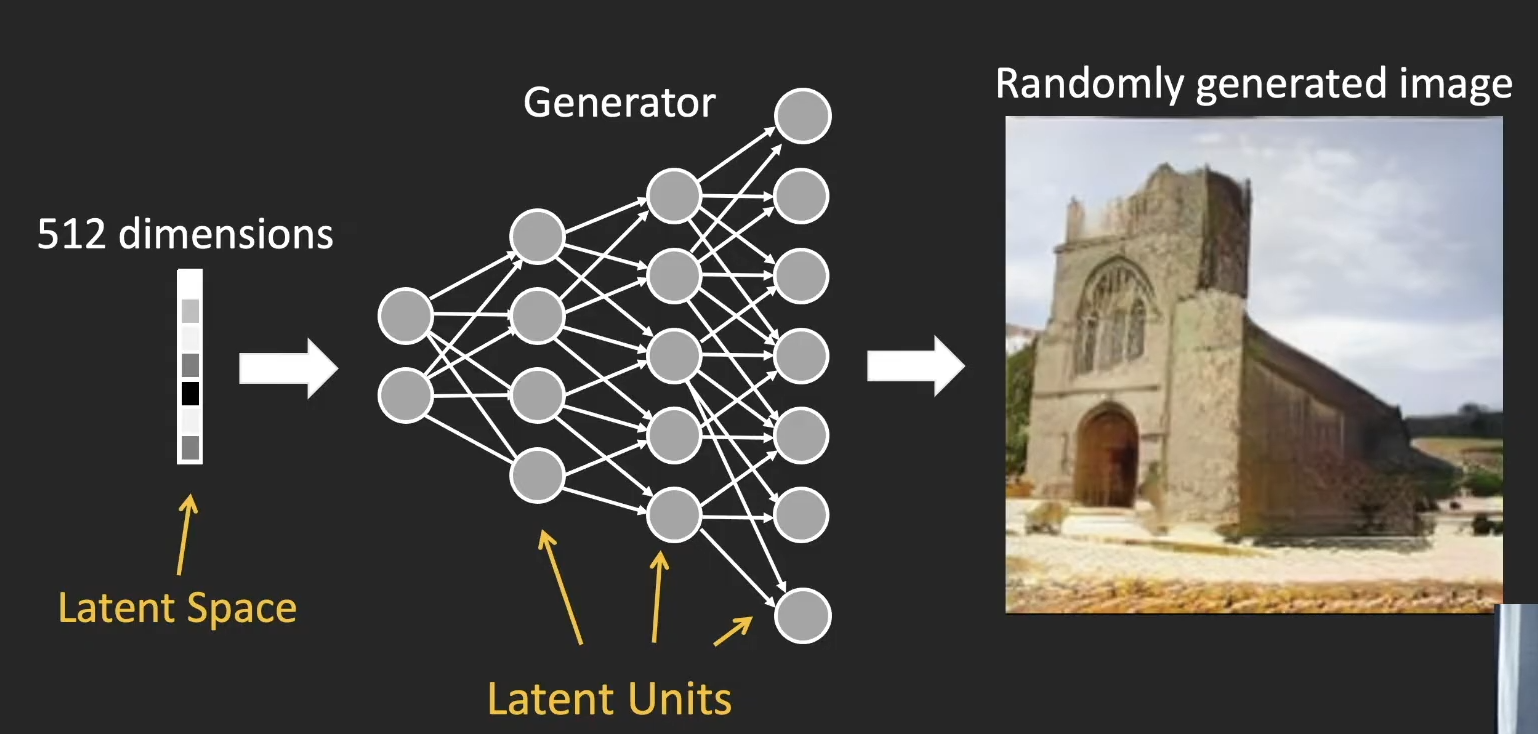
- turn on / off latent unit (GAN Dissection)
- random walk in latent space ← using attribute classifier in latent space (InterFaceGAN & GAN Hierarchy)
- layer-wise stochastic vector
→ control semantic / these using pre-trained classifier (supervised)
some unsupervised ways… (I can’t understand)
GAN inverse
want to generate image (encode latent vector) of unseen image domain
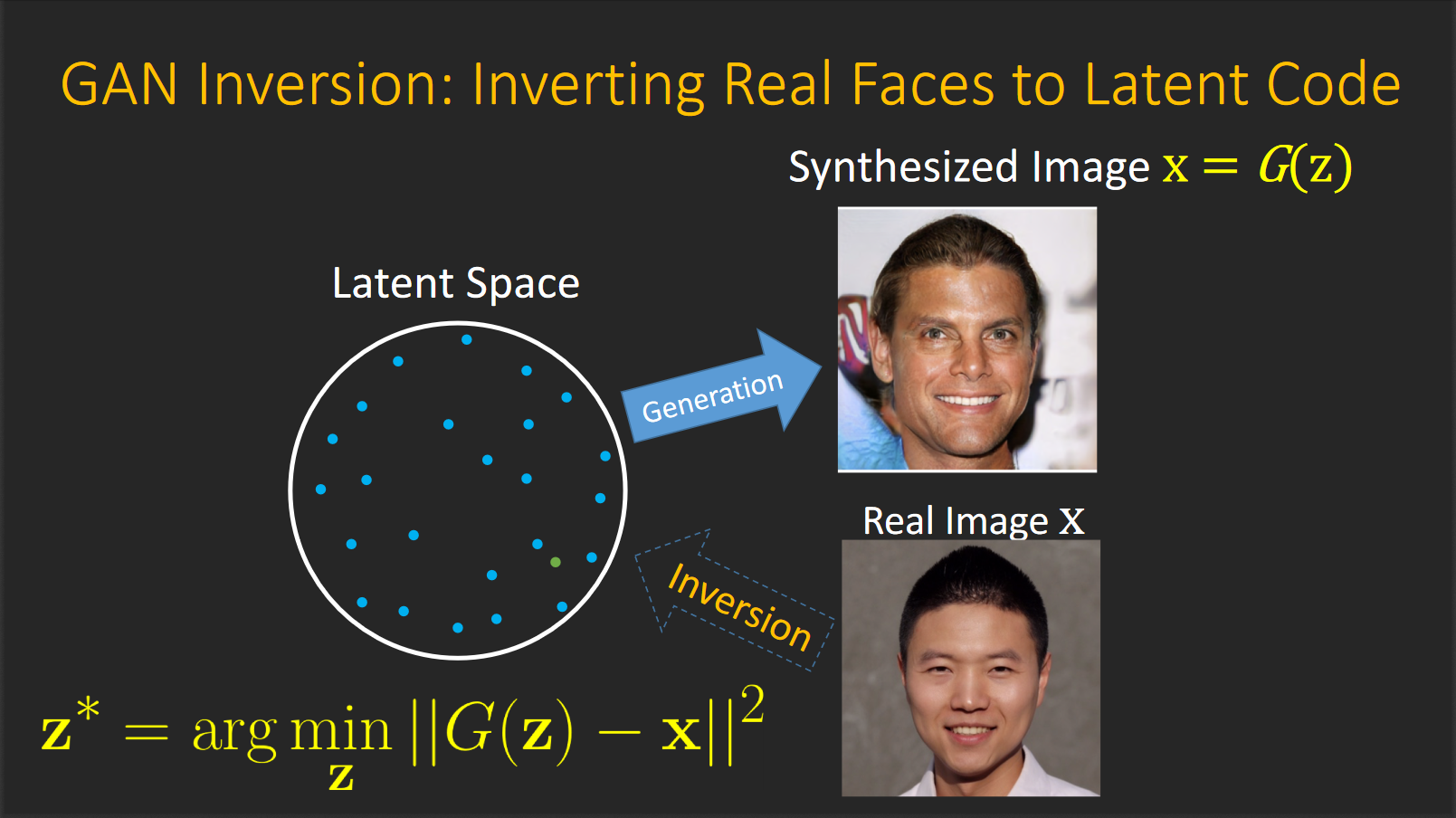
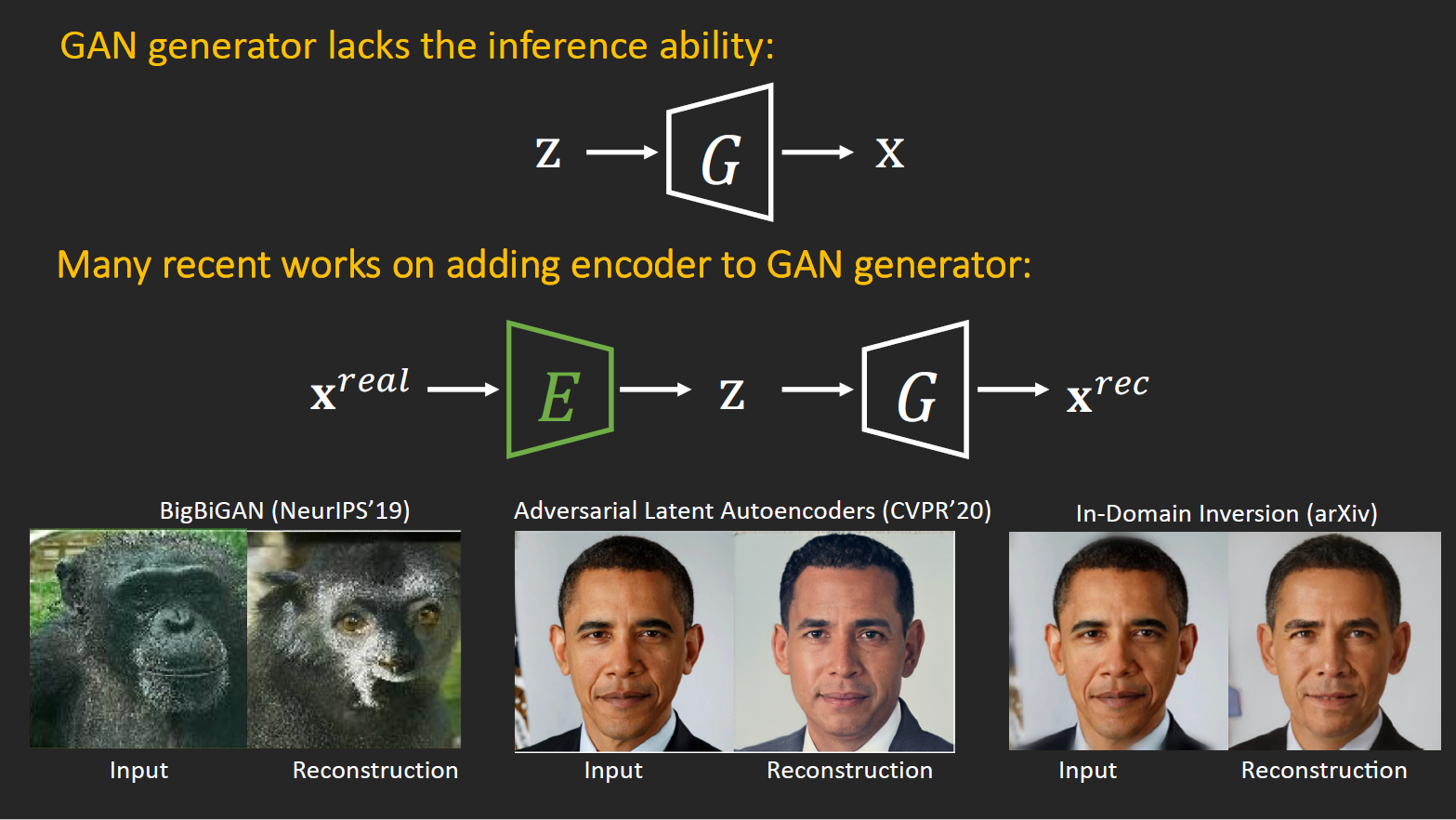
→ not works well with unseen image domain(asian, not face, etc.) (there is no constraint of encoded latent vector should in original latent domain)
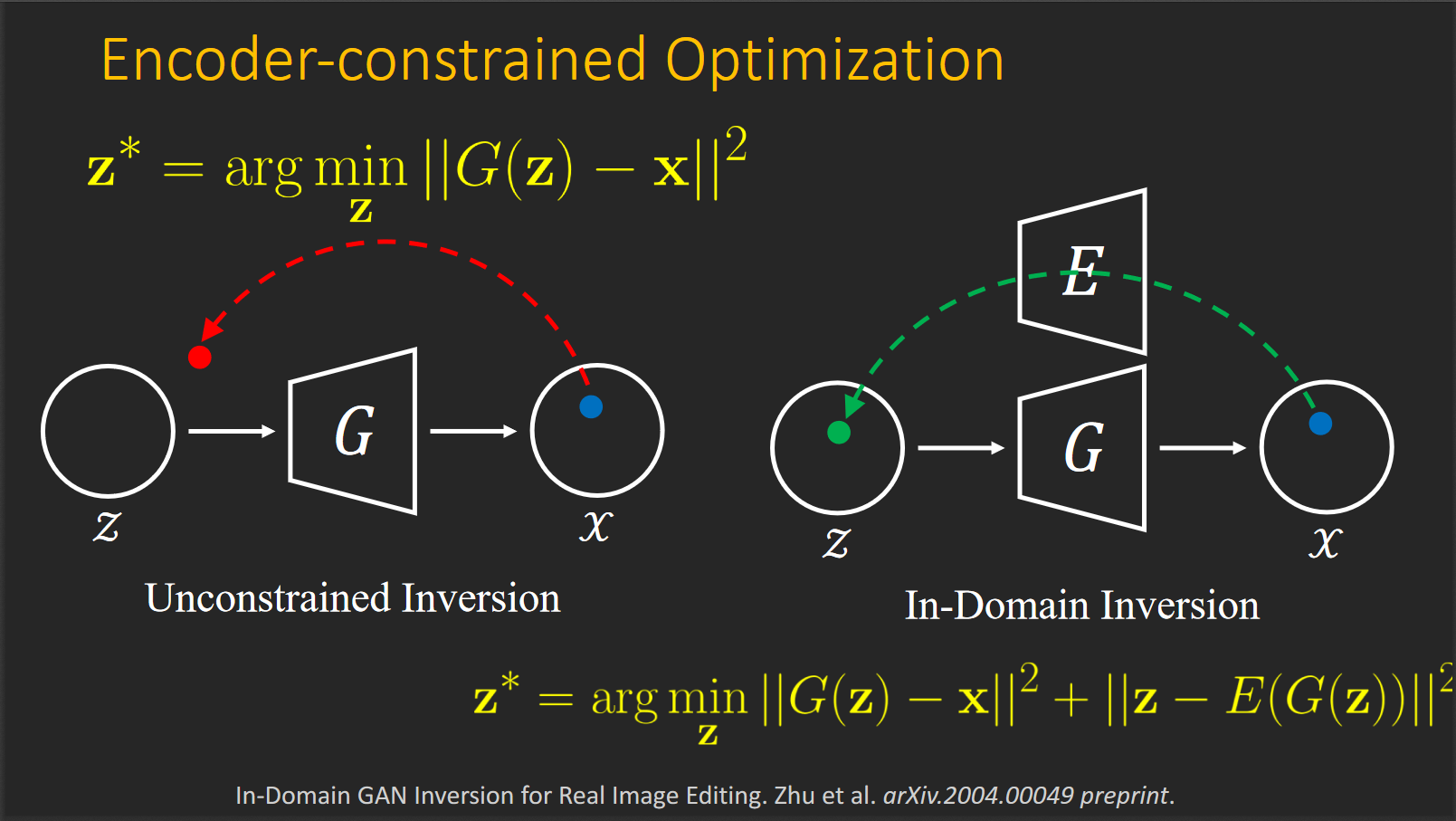
Lecture 3
Interpretability tools are crucial for high-impact, high-risk applications of deep learning.
supervised deep learning: Inputs (What is model looking at) + Internal Representation (What & how does model encode) + Training Procedure (How can we improve model)
What is model looking at
we want model not to cheat. we want model to get intuition from dataset.
→ but datasets have bias. classifier could not have intuition and just cheating the dataset.
Attribution: identify input features responsible for model decision
- Prior work:
- combine network activation and gradients ← fast but difficult to interpret
- Pertubation Approaches: change input and observe the effect on the output ← Clear meaning, but can only test small range of occlusions
- Desired Approach: automated test and wide range of occlusions
- Meaningful Perturbations: Learn a minimal mask m to perturb input x that maximally affects the networks output ← considers a wide range of occlusion sizes and shapes
- Extremal Perturbations: Learn a fixed-sized mask m to perturb input x that maximally preserves the network’s output
→ Foreground evidence is usually sufficient / Large objects are recognized by their details / multiple objects contribute cumulatively / suppressing the background may overdrive the network
Adversarial Defense

right graph: networks that are trained to get input as heatmap and to predict whether heatmap is from clean image or adversarial image can discover properly and even can recover origin label.
See the video for the details
→ Adversarial Defense is possible using heatmap!
⇒ How to use?
- Research Development: Critically design and evaluate attribution methods
- General Usage: Assume a model has failures and use attribution methods to understand them
Internal Representation
Two main way to view intermediate activations
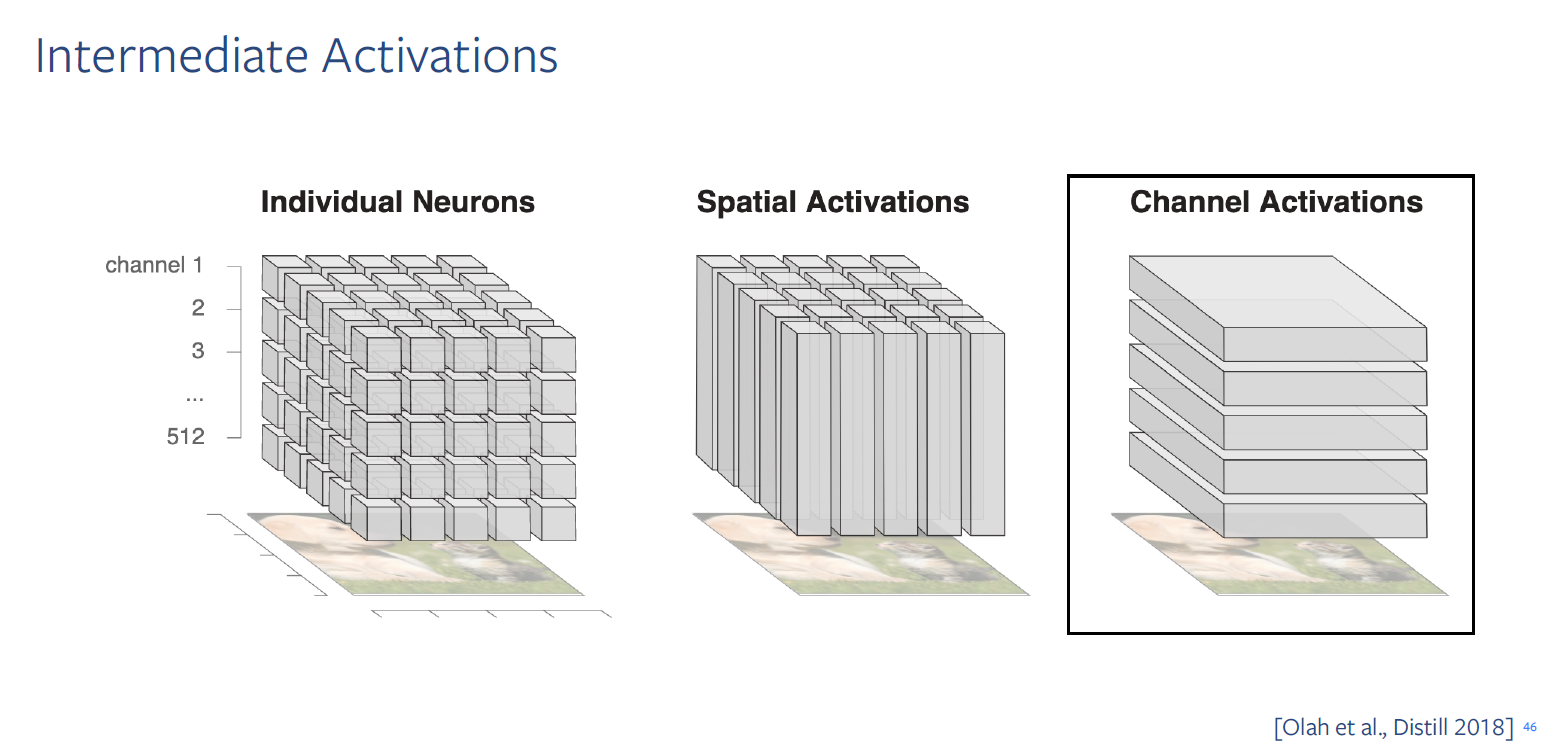
How groups of channels work together to encode? ← this is similar to how neuroscientist often don’t just study a single neuron in the brain for other coronated collections or populations of neurons
Attributing channels in intermediate activations
What groups of channels are responsible for model’s decision?
Understanding how semantic concepts are encoded
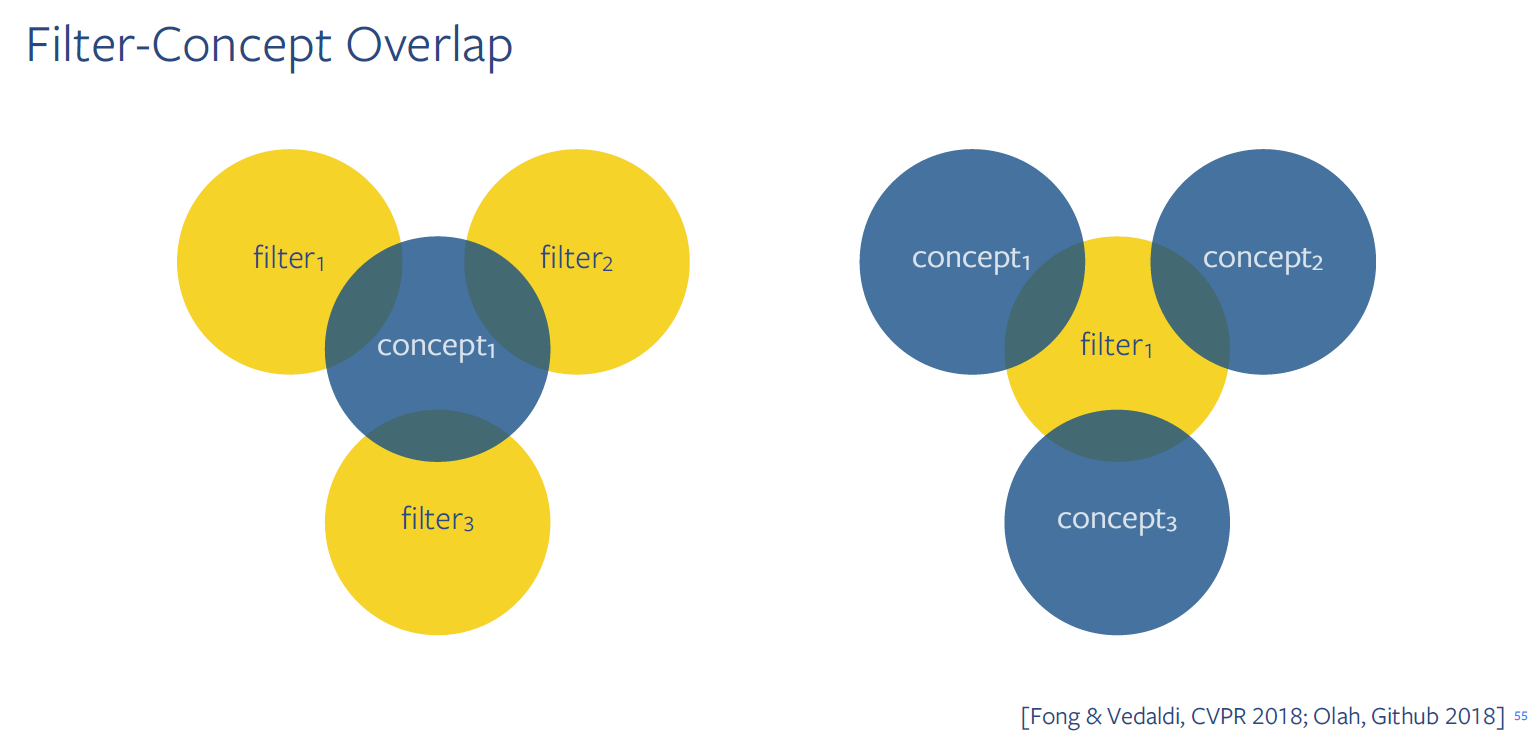
one filter might be packed with multiple concepts and one concept might be encoded using multiple fillter
Lecture 4
reverse engineering NN! ← only small fraction of interpretable NN targets for
What is understanding NN?
→ Chris think understanding of NN is kind of understanding the variable or registers in a computer program when reverse engineering it.
The weights are the actual “assembly code” of our model!
Reverse engineer a NN in two steps!
- Correctly understand all the neurons.
- Understand the weights connecting them.
Understanding Neurons
Feature Visualization (=activation maximization)
- starting from random noise, make features that stimulate neuron by gradient descent.
- https://distill.pub/2017/feature-visualization/
interrogate neurons

How do we go from understanding features to understanding weights?
Neurons are combine together and make new detector

How do we know we aren’t fooling ourselves?
Edit circuits to change model behavior

Clean room reimplementation of hundreds of neurons
over five layers, building up to curve detectors.
(Wrote a small python program that filled in the weights of a neural network)
